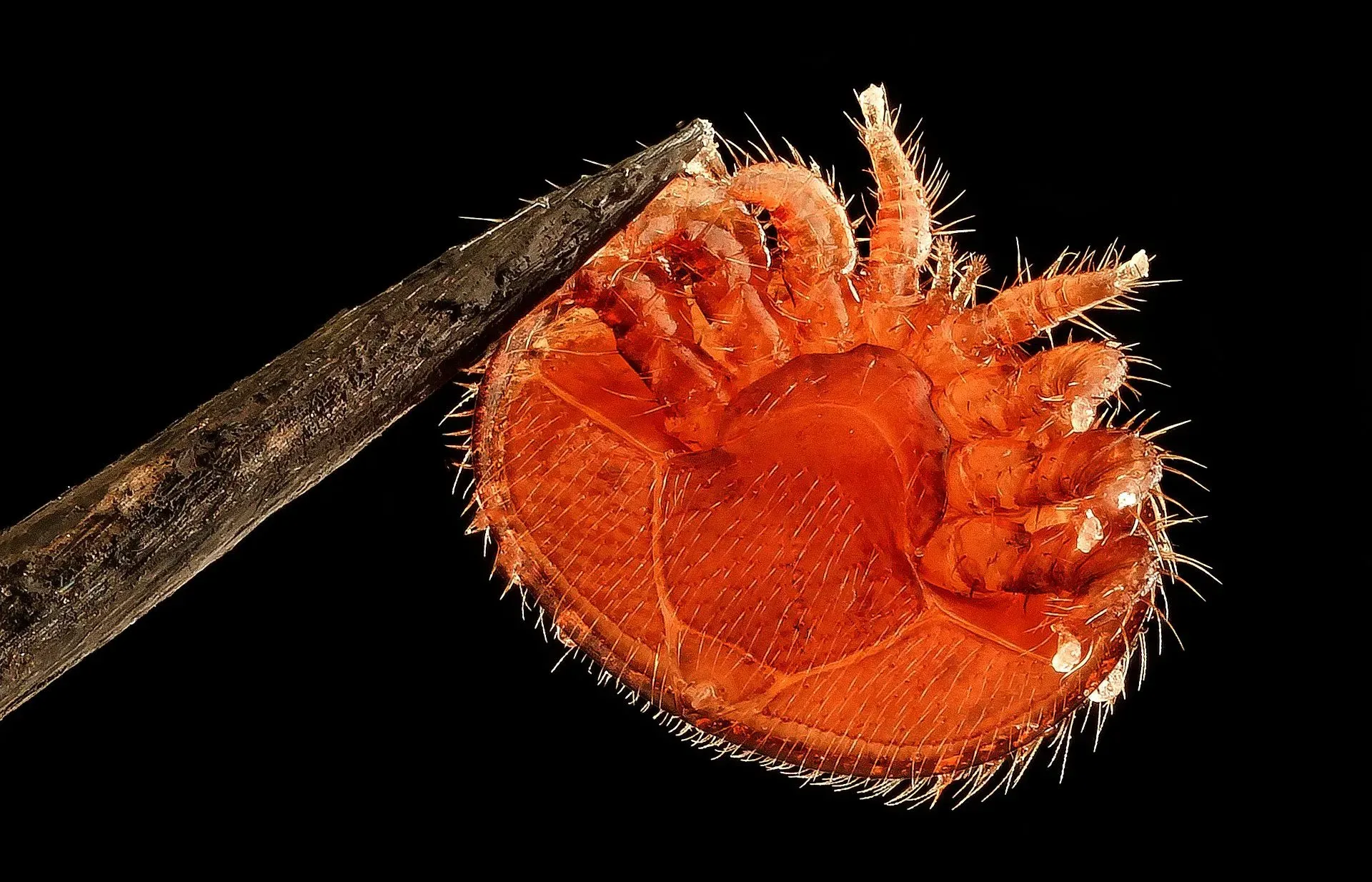
Problems we are solving
💡 Hard, frequent, unscalable work to keep bees healthy for precise pollination and food security
Bees are essential for global food security, with over 35% of food production depending on pollination. However, modern beekeeping faces complex, interconnected challenges that traditional methods struggle to address at scale.
The Core Challenge
Traditional beekeeping requires constant 👁️ Observability of bee colony through 💪🏻 Physical labor and 👁️ Time-consuming inspections. This approach becomes 💪🏻 Unscalable work as operations grow, especially for 👨🏻🚒 Industrial beekeepers managing 🏘️ Multiple apiaries at 🌲 Distant locations.
Problem Categories
🎯 Core Operational Challenges (Priority: 80-100)
Critical issues that prevent beekeeping from scaling effectively:
| Problem | Impact | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| 👁️ Observability of bee colony | Cannot detect issues early | 100 |
| 💪🏻 Unscalable work | Limits operation growth | 90 |
| 💪🏻 Physical labor | Time-intensive, seasonal constraints | 80 |
🦠 Biological Threats (Priority: 60-80)
Health challenges that can destroy entire colonies:
| Problem | Impact | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| ❄️ Overwintering collapse | Complete colony loss | 80 |
| 🦀 Infestations | Weakens colonies, spreads disease | 80 |
| 💢 Hornet attacks | Colony becomes non-productive | 70 |
| 🧶 Swarming | Production loss, management complexity | 70 |
| 🦀 Diseases | Contagious colony damage | 60 |
| 🍽️ Bee colony starvation | Preventable colony death | 60 |
| 💀 Colony with drone-laying queen | Colony becomes non-productive | 60 |
| 💢 Robbing state | Weakens colonies and loses honey | 50 |
🌍 Environmental & Systemic Issues (Priority: 30-70)
Broader challenges affecting the beekeeping ecosystem:
| Problem | Impact | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| 🌲 Distant locations | Increases inspection costs | 70 |
| 🏘️ Multiple apiaries | Management complexity | 50 |
| 💢 Aggressive bee colonies | Safety and management issues | 50 |
| 🌻 Monocultural agriculture | Reduced bee nutrition diversity | 40 |
| 🤢 Pesticide poisoning | External toxicity threat | 40 |
🛡️ Ethical & Welfare Concerns (Priority: 40-50)
Issues related to bee welfare and sustainable practices:
| Problem | Impact | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| 💀 Alcohol washing killing bees | Unnecessary bee death | 50 |
| 💀 Intrusive inspections | Stress and disruption to colonies | 50 |
🏗️ Infrastructure & Knowledge Gaps (Priority: 20-40)
Supporting challenges that affect industry development:
| Problem | Impact | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| 🎒 Challenging to become a new beekeeper | Reduces industry growth | 40 |
| 📦 Warehouse organization | Operational inefficiency | 30 |
| 🗃️ Poor hive ventilation | Equipment design issues | 30 |
🌪️ External Threats (Variable Priority)
Unpredictable challenges requiring resilient solutions:
Emerging Challenges We're Addressing
🌡️ Climate Adaptation
- Shifting bloom periods disrupting pollination timing
- Extreme weather events increasing colony stress
- Changing migration patterns affecting wild pollinator interactions
💰 Economic Pressures
- Rising equipment and land costs
- Market volatility in honey and pollination services
- Cost barriers for adopting monitoring technology
📊 Data & Integration
- Fragmented data across different farm management systems
- Privacy concerns with continuous hive monitoring
- Need for standardized metrics across the industry
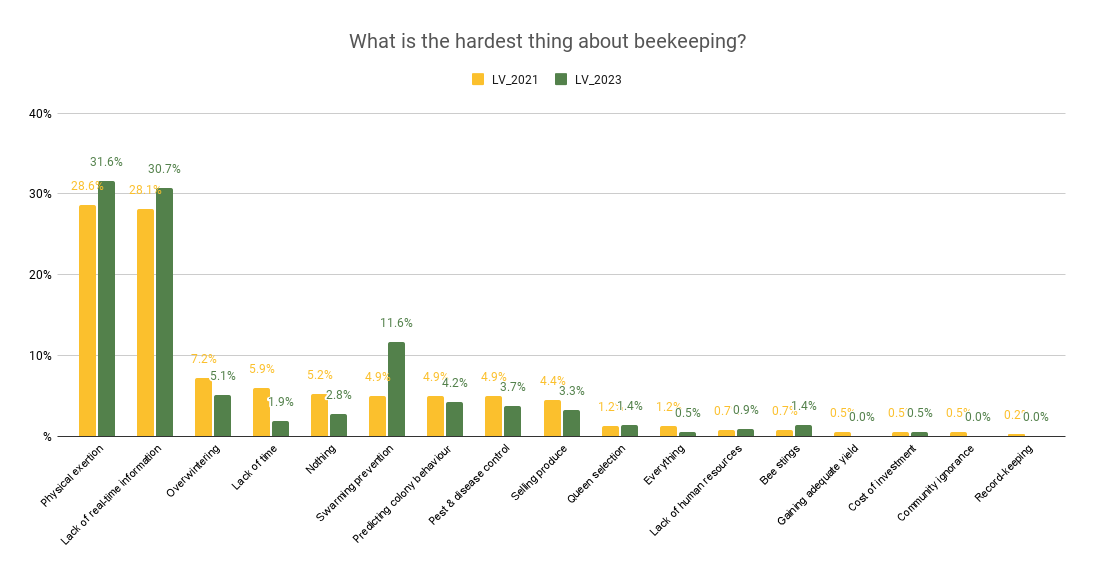
Survey by BeeSage, source
Our Approach: Technology + Ethics
Unlike solutions that focus solely on data collection, we prioritize:
- Bee welfare first: Technology should reduce stress on colonies, not increase it
- Practical impact: Focus on problems that beekeepers actually face daily
- Scalable solutions: Address root causes that prevent industry growth
- Open innovation: Share knowledge to benefit the entire beekeeping community
Note: We maintain a detailed problem database to link specific issues with solution features. This systematic approach ensures our technology development addresses real beekeeping challenges rather than theoretical problems.
